Laptops, thermal printers, and other compact electronic devices need small-size storage drives to optimize space. Mini-SATA or mSATA is a smaller form factor of the Seria ATA (SATA) interface for Solid State Drives (SSDs). Today, mSATA SSDs are widely available from a wide range of manufacturers including but not limited to Toshiba. Samsung, and HP. Let’s look into the types, workings, architecture, and definition of mSATA interface in more detail.
What is mSATA?
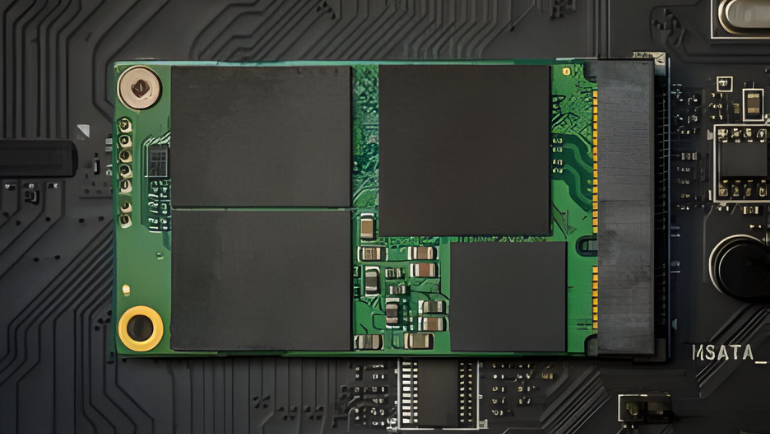
Serial ATA International Organization (SATA-IO) released the mSATA specification for SSDs in September 2009. mSATA emerged in 2011 as part of SATA revision 3.1 for enterprise use. Mini-SATA is a mini version of the SATA interface having the same speed but lower storage capacities.
It is a lightweight SSD with a dimension of 50.8 mm x 29.85 mm x 4.85 mm. Initially, mSATA was adopted by laptop and ultrabook as a compact SSD solution. Over time, it became popular among other applications such as embedded systems, industrial PCs, and compact computing devices.
Mini-SATA Architecture
mSATA is a form factor primarily used for SSDs that connect to the motherboard directly without a cable. SSDs using mSATA form factor consist of a controller, NAND flash memory cell, and sometimes DRAM similar to a standard 2.5” SSD drive. It follows SATA bus protocols and uses different NAND flash memory cell types such as SLC, MLC, QLC, or TLC for industrial applications.
The controller acts as a main communication bridge between the computer (host) and the NAND flash chip on the drive. Whereas, the DRAM functions as cache memory for faster transfer speed and data access.
Types of mSATA

mSATA is a versatile form factor employed in different devices such as wireless cards, and SSDs. Based on function and cell type, mSATA can be categorized into two primary types, each briefly explained below:
mSATA Types Based on Function
mSATA form factor is versatile and performs various functions on different systems. Here are some applications of mSATA form factor in different devices.
- mSATA wireless cards: laptops use mSATA wireless cards for wireless connectivity. However, most newer laptops now have integrated wireless capability in motherboards.
- mSATA SSDs: Most common types of mSATA devices available widely in the market. It is used in compact laptops and thermal printers for storage needs.
mSATA Types Based on NAND Cell Types
NAND flash cell in mSATA drives varies with performance, endurance, and cost. Each type of cell defines mSATA drive uses and suitability in workload. The following section will explain different NAND flash types in mSATA drives.
- SLC mSATA SSD: Uses Single-Level Cell NAND flash, and offers high performance, reliability, and endurance. It transfers data one bit per cell for faster speed.
- MLC mSATA SSD: Provides balanced performance using multi-level NAND cells, transferring data two bits per cell.
- TLC mSATA SSD: Three bits per NAND cell data transfer, best for capacity and affordability. It uses a triple-level NAND cell to maximize storage space and affordability but with lower endurance.
- QLC mSATA SSD: Huge capacity at the lowest cost with Quad level NAND cells offering 4 bits per cell. It has the lowest price among other cell types but at the price of drive endurance.
This mSATA type is specific to only SSDs and not wireless cards.
How Does mSATA Work?
The working of mSATA Solid State Drives consists of two operations: read and write. All communication between the host system and mSATA SSD drives happens via the SATA bus and mSATA controller. For write operations, the mSATA controller writes data onto a DRAM or NAND memory chip. If written on DRAM it accelerates the writing process or else no change in speed occurs. mSATA controller, during write operation, uses wear leveling and error correction protocol to extend SSD lifespan.
In read operations, the data is checked on the DRAM (for faster access) if not available, then fetched from the NAND chip. All processes are done via mSATA controller and SATA busses.
Relationship Between mSATA vs. SATA Interface
SATA is an interface or bus that communicates with the host system and drive. In contrast, mSATA is a form factor design for but not limited to SSDs following SATA protocols. It’s important to note that mSATA sends and receives data through the SATA buses. Also, all three SATA buses: SATA 1, SATA 2, and SATA 3 are compatible with the mSATA form factor. SATA and mSATA both follow the same principle of communication and only differ based on size, capacity, and speed.
The Need for mSATA SSD Interface
mSATA SSDs were needed for compact devices such as ultra-thin laptops or thermal printers that can’t incorporate a 2.5-inch SSD. mSATA form factor in SSDs was designed to be lightweight and compact for ultra-thin computer devices. Today, mSATA SSDs are commonly used in GPS, notebooks, laptops, and other industrial applications.
However, due to limited capacity, SATA-IO introduced RAID technology in mSATA drives for shared speed, and capacity. Many mSATA Raid controllers and mSATA Raid adapters are available on the market for enterprise applications. Also, these drives are used as cache memory for better data access speeds.
Features of mSATA Drives
Here are some features in mSATA drives that optimize your system performance.
- Speed: The speed can reach around 551 Mbps for read operations and 304 Mbps during write operations. Whereas, the total bandwidth of mSATA drives is around 6 Gbps.
- Capacity: Ranges from 8 GB to 512 GB storage capacity, and can exceed 2 TB due to 3D NAND technology.
- Reliability: Lifespan of mSATA drives is between 1.5 to 2 million hours of read/write operations. Protective case adds protection from resistance and external shock.
- NAND Cell Type: Multi-level, Single-level, and other NAND cells in mSATA drives for read or write-intensive operations.
- Smart Features: It uses bad block management, TRIM command, and garbage collection to increase drive efficiency.
- Monitoring: Many tools such as “S.M.A.R.T monitoring”, help check drive temperature and Program/Erase (P/E) cycles.
- Error Correction Code (ECC): Prevents errors in writing data onto the mSATA drive, making the write operation more efficient.
Uses of mSATA Drives
Businesses have many uses for mSATA SSD drives, some of which are mentioned below.
- Compact Devices: mSATA form factors are still used in printers, laptops, and other compact devices like tablets.
- Embedded Systems: Many embedded industrial-grade systems utilize mSATA drives for reliable data storage.
- Networking Device: Routers or switches may employ mSATA drives for various operations like logging, caching, and more.
- Cache Memory: mSATA SSD drives are sometimes used as cache memory for faster data retrieval in systems like laptops, and printers.
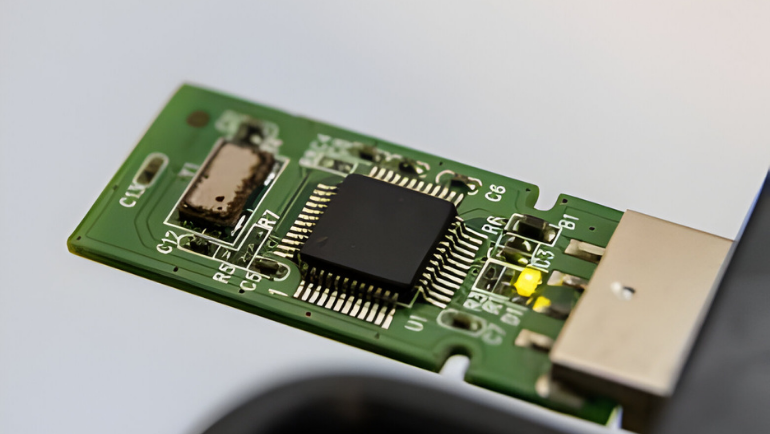
- Portability: With an mSATA to USB 3.0 adapter card, the mSATA drive can also be used as a portable USB flash drive.
Pros and Cons of mSATA Drives
All technologies have pros and cons based on workload requirements. Let’s look into some of them briefly.
| Pros | Cons |
| Compact Size: Ideal for small form factor devices. | Compatibility Issues: Due to their compact size, not all motherboards support mSATA drives. |
| Energy Efficient: Lower mSATA power consumption than other drives. | mSATA Price: It is more expensive per GB than other 2.5-inch SATA drives. |
| Easy to Install: No wires are needed for connection. | Limited Speed: All mSATA drives are limited to SATA 3 protocols only. |
Future of mSATA Interface
With its lower power consumption and smaller size, the Mini-SATA gained traction with many industrial applications. It provides high speed in a rugged environment and offers effective performance boasts. Many features including ECC, wear leveling and SMART monitoring are up to today’s storage standard. However, The mSATA form factor has grown slightly outdated due to the rise of M.2 form factor.
M.2 form factor comes in PCIe, M.2 SATA and M.2 NVMe interfaces, breaking the speed limitation of mSATA form factor. This is why, M.2 form factor is slowly replacing mSATA drives in devices that require faster processing power. Newer devices like laptops and motherboards widely use M.2 slots rather than mSATA while many older devices still use mSATA drives.
Best mSATA Drives for Sale
Small Enterprises and Businesses (SMEs) buy storage devices like mSATA SSDs for data storage in rugged environments. These drives offer fast speed, smart features, and high read/write cycles, making them best for resource-intensive operations. mSATA price ranges from $59 to $3,999.
It varies based on model, NAND cell type, capacity, and other factors. Computing Worlds provides the best deals and discounts on Solid State Drives for sale. Mention below are some of the best mSATA devices available on our website.
Bulk quote inquiries are also available for the required number of mSATA drives.
FAQs
Is mSATA Obsolete?
No, mSATA is still widely used in printers, POS, and other compact devices. However, the M.2 form factor uncapped speed has an upper edge over mSATA.
Can I Convert 2.5″ SSD to mSATA?
Yes, you can convert 2.5” SSD to mSATA via an mSATA to SATA adapter or converter. It allows you to fit mSATA drives into a 2.5-inch SSD enclosure.
Is mSATA the Same as Mini-PCIe?
No, mSATA and mPCIe interfaces are unrelated interfaces with different electrical signals and should not be confused together.
Is mSATA Faster than 2.5″ SSD?
No, mSATA and 2.5” SSDs have similar read/write speeds. However, the speed may vary with different SSD models and protocols.
This marks the end of all about mSATA form factor. As NAND flash manufacturers evolve the technology the way we store data will change as well. Therefore, it’s important to understand different flash interfaces like SAS and SATA to be one step ahead of the competition. But, if you belong to a business where data integrity is crucial, opt for Opal 2.0 Self-Encyption Drive (SED) for better data security. To have a cost-effective storage solution enterprises employ both Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) and SSDs to better capitalize on their investment.
For more information about storage drives and their different technology, stay connected to Computing Worlds blogs.






