- Form Factor
- Capacity
- Speed
- Performance
- Gaming
- Life Span
- Power Consumption
- Data Recovery
- External HDD vs. External SSD
- Pricing
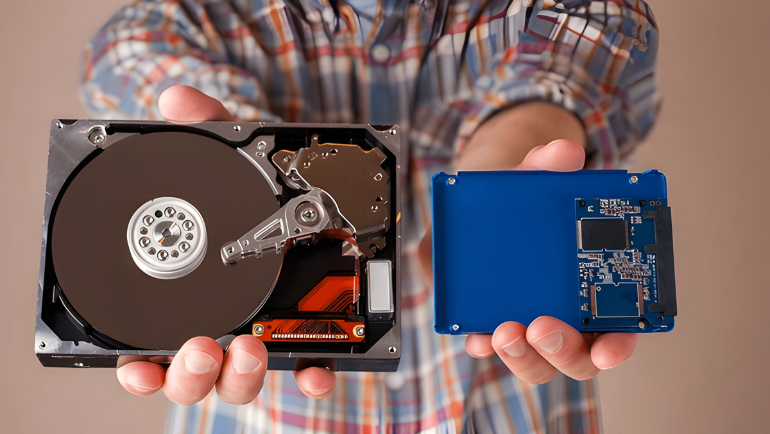
Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) and Solid-State Drives (SSDs) are both storage devices widely used in modern-day computers. Storage devices are becoming more advanced, and new models of both SSDs and HDDs are coming into the market with better storage capacity and speed. However, HDDs are old yet tested technology, whereas SSDs are faster and a new addition to the storage world, making it challenging to select one over another. Check the SSD vs. HDD difference in detail to help you make an informed decision.
Difference Between SSD and HDD
SSDs and HDDs are highly in demand due to their various business benefits. Here we compare SSD and HDD in detail to understand which one is best for you.
SSD vs. HDD: Form Factor
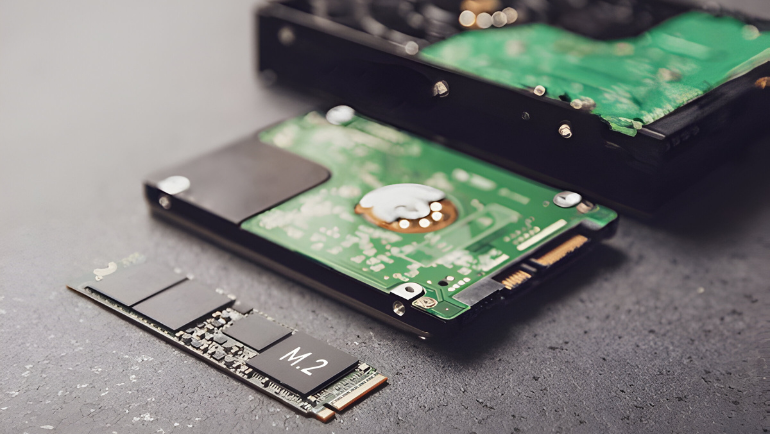

SSDs were first designed to resemble the most popular HDDs in size and appearance. These days, many SSDs are relatively compact due to the compact size of NAND flash chips. However, HDDs are bulky and take up more space on your motherboard, making it difficult to optimize or include other storage devices. SSDs, such as the U.2, mSATA, M.2 SSD, and 2.5-inch Standard SSD, while HDDs come only in 3.5-inch and 2.5-inch form factor. The biggest advantage of M.2 SATA or NVMe SSDs is that they save space and attach directly to the motherboard without cables.
SSD vs. HDD: Storage Capacity and Availability
SSD storage capacity ranges from 128GB to 15TBs and more, however, the larger sizes are hard to find and super expensive. On the other hand, you can get an HDD with capacities between 80GB to 30TBs which are easily available for resource-intensive enterprise workloads. Enterprises and businesses buy SSDs to speed up operational tasks, whereas HDDs are preferred for storing bigger data.
SSD vs. HDD: Speed
Speed is the real game-changer in the difference between HDD and SSD drives. The speed on an HDD can vary from 80 to 120 MB/s, whereas on SSD, it can go from 350 MB/S to 600 MB/S. SSDs’ flash memory allows them to write and read data more efficiently and bring it to the processor for instant processing than HDD.
SSD vs. HDD: Performance
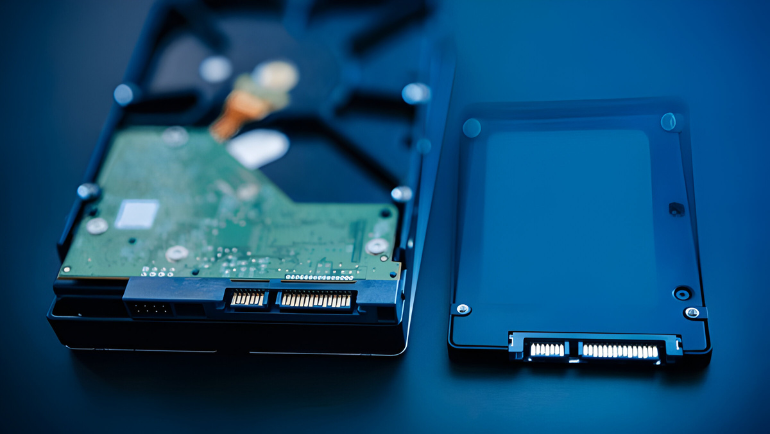

Performance plays a vital role in everyday devices and computers. That said, performance is essential in selecting storage devices like HDDs and SSDs. HDDs are mechanical and have moving parts making them relatively slower than SSDs. Since SATA, Sas or NVME SSDs are made up of flash memory chips, and don’t have moving parts, you can get a significant boost in speed. This enhances overall system performance like boot-up time and app opening time than conventional magnetic disk drives.
SSD vs. HDD: Gaming

For Gaming, an SSD is a straight win over an HDD because it has flash memories that result in better loading time and faster data retrieval. As games become increasingly complex, with large open worlds and detailed textures, SSDs’ fast data transfer speed is a clear winner. On the contrary, HDDs offer you a larger storage capacity than an SSD at an affordable price, but you will experience a longer load time and lower frame rates. In contrast, an SSD can significantly reduce load times, allowing you to jump into the game quicker and spend less time waiting at loading screens.
SSD vs. HDD: Life Span and Durability

SSDs and HDDs can survive up to 5 years or longer, but SSDs if taken properly can outperform in terms of lifespan. This is because HDDs have spinning disks that may eventually wear out, whereas SSDs have no moving parts but limited write cycles. However, the HDD and SSD lifespan can be extended if protected from falls, Electro Static Discharge (ESD), or damage.
SSD vs. HDD: Power Consumption
An HDD has a moving plate or spinning disk and arm which requires a decent amount of power to perform read/write operations. On average, HDDs consume between 5.7 and 9.4 watts of power. While this may seem insignificant, it can add up over time, especially if you constantly read and write data. In terms of HDD and SSD power consumption, SSDs are more power efficient than conventional hard disks, particularly when idle. Usually, an SSD consumes 0.2 watts in the idle state and can go up to 8 watts depending on the usage. This is due to the flash memory technology that consumes less energy than HDDs.
SSD vs. HDD: Data Recovery
The data on the HDD is stored physically on the platter until new data overwrites it. So, recovering and extracting the data is much easier on an HDD than on an SSD. In General, data recovery is easier on an HDD because the data used in hard disks favors it. In contrast, SSD stores data in NAND flash memory as eclectic charges, making it difficult to recover it. However, recovery is often possible, but the probability is not as good as in HDD.
External HDD vs. External SSD

External HDDs are a much more affordable choice for data storage; you will get larger storage capacities at a lower cost per gigabyte. However, they’re significantly slower due to spinning platters and a read/write head. Businesses prefer HDDs for high-capacity storage servers. Enterprises also choose external SSDs for their blazing-fast speed, lightweight, and durability. High-speed external SSDs connected via Thunderbolt are perfect for High-intensity tasks. You can edit videos or transfer huge files right on the drive and take them wherever you want. Moreover, if you have any spare HDD or SSD you can use them as portable drives with a case that converts your conventional drive into an external drive.
SSD vs. HDD: Pricing
Pricing of both storage devices can be a deciding factor, as HDDs are more affordable than SSDs. You can get a 500 GB hard drive for the price of a 128 GB SSD. Computing Worlds has a wide range of SSDs and HDDs to choose from.
Popular HDDs and SSDs
Businesses buy storage devices that provide them value for money from popular IT hardware brands. Here are the top SSDs or HDDs that you can buy at Computing Worlds.
Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
Solid State Drive (SSD)
You can also request a bulk quote online for the required SSD and HDD.
Frequently Ask Questions:
What is the Difference Between SSD and HDD?
HDDs store data on magnetic drives, whereas SSDs store data on flash memory chips. This makes SSD a better storage option for operating systems, highly intensive applications, games, and more.
Is SSD Faster than an HDD?
An SSD is almost six times faster than a conventional HD drive, making it a better choice for most users.
Can a Laptop Have Both SSD and HDD?
Indeed, you can use SSD and HDD together in a single system. Overall, the actual use of the drives is the main deciding factor, whether you prefer speed or capacity.
SSDs are fast and expensive, but hard drives offer more capacity for keeping your files. Unlike hard drives, SSDs are lightweight and durable and will not take damage from drops and vibration. Moreover, SSDs come in multiple cell layers like QLC and TLC SSDs knowing their differences will further help you in finding the best storage device. This marks the end of our debate between SSD vs. HDD storage devices.
For more such information, stay tuned to Computing Worlds Blog.