System downtime can lead to reputational damage, regulatory fines, and revenue losses. Hot swapping solves this problem by allowing the removal of redundant modules like storage drives or power supplies without disruption. Today, Hot swapping is an integral part of high-availability systems, including large-scale data centers, financial institutions, and real-time communication platforms. This section will help you understand hot swapping and why it is important.
What Is Hot Swapping?
Hot swapping is a feature used to replace a device while the system is running. It is desirable when repairing or configuring a system without downtime or abruptions. Depending on the application, a user can configure the components automatically or manually. Hot swapping is used interchangeably with hot-plugging, but there is a difference. Hot Plugging refers to the addition of a component, while hot swapping is the replacement.
How Does It Work?
Hot swapping works by replacing flawed or failed hardware components without disruption. That said, the redundant unit automatically takes over when a device fails in the system. Hot swap provides a space like a rack or enclosure for the device, which creates an uninterrupted connection during replacement. Various interfaces support hot-swapping features, including SCSI (Small Computer System Interface), LAN (Local Area Network), and IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics). Also, Hot-swap storage devices usually work with RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disk) configuration, which splits data into multiple drives.
Hot Swapping Devices
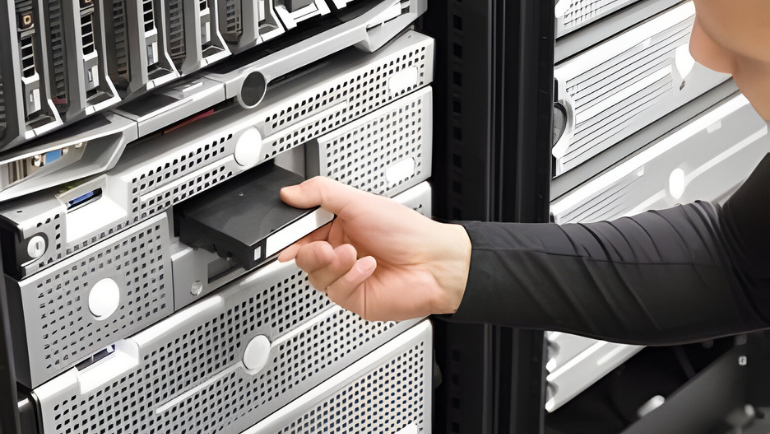

Hot swapping devices are compulsory in mid to high-end machines. They prevent static shock between the system and components and provide flexible maintenance. Also, the plug-and-play feature in most hot swapping devices makes it user-friendly and easy to configure.
Types of Hot Swapping Devices
Hot-swappable components like keyboards, USBs, fans, power supplies, CPUs and GPUs are commonly used in enterprises. Here are a few prominent devices:
- Storage Drives: The hot-swappable redundant storage arrays in high availability systems allow drive replacement without turning off the system. SAS, NVMe and SATA are the most popular hot-swappable storage drives.
- Power Supplies: Parallel connection minimizes power disruption risk. That said, if one component fails, the other one takes its place, which ensures operational continuity.
- Network Interface Cards: Shared devices on the network are not interrupted during replacement.
- Cables & Modules: Hot swapping lets you swap out broken cables and modules without disrupting the network connection.
Popular Hot Swapping devices
Hot swap devices are essential for a high-performance system that runs 24/7. Computing Worlds offers a wide variety of popular hot-swapping devices in bulk for sale.
- SDSDXPA-512G-G46 SanDisk Card
- SDSDXN-128G-G46 SanDisk Card
- PA-5220 Palo Alto Networks Firewall
- 0711V0 Fan
- 7N67A00882 Power supply
You can also request a bulk quote online for the required hot-swapping devices.
Benefits of Using Hot Swapping
When it comes to safety and efficiency in high-end systems, hot swapping provides the best approach. Let’s explore its key benefits.
- Scalability & Efficiency: The faulty components can easily be replaced & troubleshooted without shutting down the system. It mitigates system delay and provides a wider range of scalability options
- Flexibility & Data Loss Protection: Hot swapping provides the flexibility to configure & change the system without interruption. It also reduces the risk of data loss from electrical sparks between the system & components
- Easier Device Management: You can add or remove components without having to configure them manually, making device management easier
Challenges of Using Hot Swapping
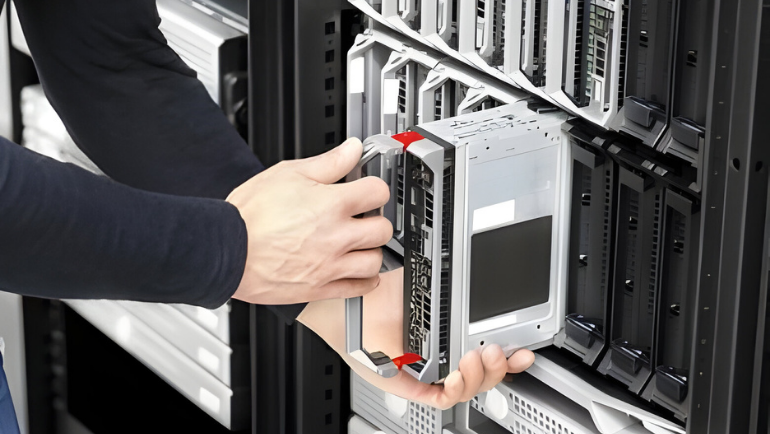

While hot swapping offers many benefits, it’s not without its challenges. Here are some common problems users encounter in hot swapping.
- Compatibility: Not all hardware and systems support hot swapping. That said, for seamless operation, both the system and components must be compatible
- Safety Precautions: Hot swapping requires careful adherence to guidelines and safety precautions to prevent accidents. Therefore, perform hot swapping only at non-hazardous locations, and wear gloves
- Data integrity: Unexpected accidents can lead to data corruption. That’s why it is important to backup data and place recovery measures for extra protection
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is a SATA Hot Swap?
It is the ability of SATA drives to resist electrical discharge due to a microchip installed in it.
What is a Hot Swap in BIOS?
Hot swap-supported motherboards have the option to enable & disable the hot swap feature in BIOS.
How to Enable the Hot Swap for SATA Storage Drives?
To enable the hot swap feature, follow the instructions:
- Open ‘BIOS’
- Navigate to ‘storage’ or ‘SATA configuration’
- Enable ‘SATA hot swap’ or ‘hot swap’
For high-availability enterprises, minimizing downtime is critical. However, lengthy configuration and frequent updates reduce efficiency & performance. Therefore, plug-and-play features of hot-swappable devices allow easy maintenance and require no configuration. It eliminates system delay while maintaining peak performance. Enterprises opt for both hot swapping and hot plugging devices to create a mission-critical environment. You can easily find hot swappable PCs and servers by CTO or BTO customization from various popular IT hardware brands.
For more updates on various device features stay connected with the Computing Worlds blog.